9- A&P - Define:
Caudal - towards the feet
Cephalic - towards the head
Cytoplasm - liquid of the cell inside the cytoplasmic membrane and outside the nucleus
Sagittal - another term for midline
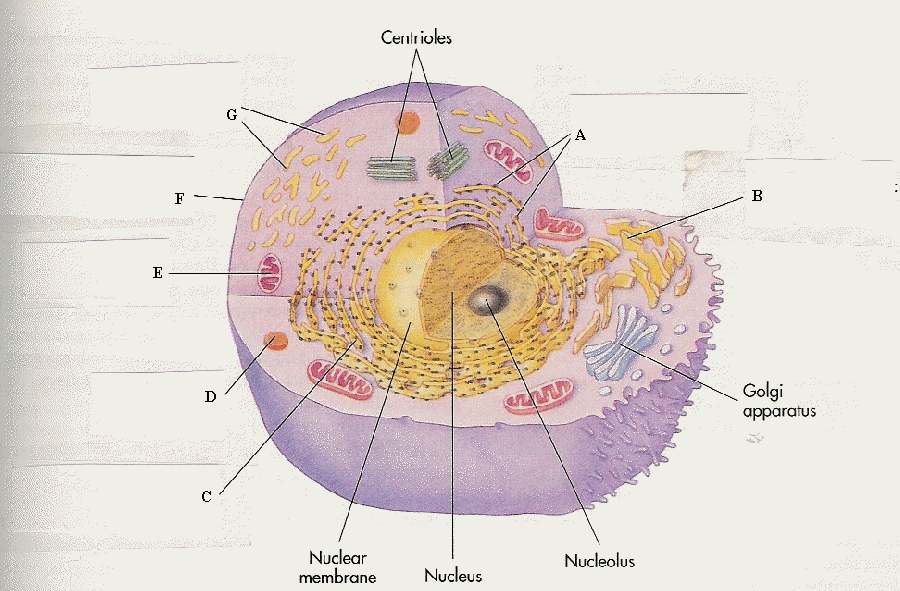
10-A&P - Use the picture below. List the structure and define its main purpose
A - ribosomes - protein factory
B - smooth endoplasmic reticulum - produces lipids and carbohydrates
C - Rough endoplasmic reticulum - robosomes attach to rough.
D - Lysosome - digestive system of the cell
E - Mitochondrion - Adenosine triphophate powerhouse
F - Plasma Membrane - boundary of the cell, marker proteins attach
G - Smooth endoplasmic reticulum - produces lipids and carbohydrates
11-A&P - List the three types of tissues in the body and give one example where in the body it is found.
Epithelial - glands, digestion, outside skin
Connective - fat, cartilage, bone
Muscle - smooth, skeletal, cardiac
Nervous - electrical signals, neurons
12-A&P List the 6 main types of joints.
plane or gliding - saddle, hinge, pivot, ball & socket, ellipsoid
13-A&P - Muscle contractions are labeled as isometric and what is the other one?
14-A&P - What is the difference between afferent diversion of the nerves.
afferent sensory to CNS and efferent sensory CNS to body.
15-A&P - What is the purpose of the liver?
iron metabolism, plasma protein production, detoxification of drugs and matter.
16-Pathophysiology - Intracellular fluid (ICF) is found inside all body cells and accounts for 40% of total body weight. Extracellular fluid (ECF) is the fluid found outside the cells and is further divided into intravascular and interstitial compartments. ECF accounts for 20% of total body weight. Interstitual fluid accounts for about 15% to 16% of total body weight.
Define the following: numbers 17 thru 25
17 Solutes - substance
18 Solvent - Fluid
19 Osmosis - flow of fluid from low concentration to high concentration
20 Hypertonic - cause cells to dehydrate
21 Hypotonic - cells burst or swell
22 Diffusion - molecules move from high to low
23 Active transport - substances move again the concentration. low to high. Energy
24 Facilitated diffusion - moves substances in or out of cells from higher to lower. No energy
25 Hypokalemia - low potassium
Are the following electrolytes positive or negative?
26 - Potassium +
27 - Calcium +
28 - Magnesium +
29 - Sodium +
30 - What does this mean? Resp Alkalosis
¯CO2 + H2O ® ¯H2CO3 ® ¯ H+ + HCO3-
31. ¯H+ + HCO3- ® ¯H2CO3- ® H2O + ¯CO2 Metabolic Alkalosis
32. CO2 + H2O ® H2CO3- ® H+ + HCO3- Resp Acidosis
33. H+ + HCO3- ® H2CO3- ® H2O + CO2 Metabolic acidosis